Buy hafnium at Golden Gates
Even small amounts of this technology metal are responsible for major innovations: Hafnium makes computers faster, aircraft parts more robust and nuclear power plants safer.
PROPERTIES
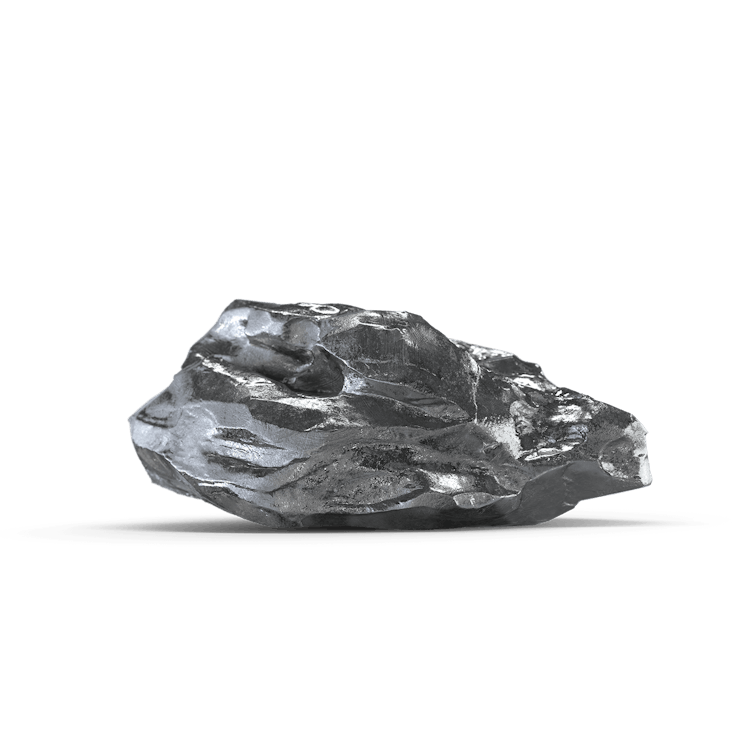
Hafnium is a silvery-white, lustrous, readily malleable metal. Its physical properties depend strongly on any zirconium impurities. If it possesses a high degree of purity, it is comparatively soft, pliable and thus easy to work with. The more traces of oxygen, nitrogen and carbon it contains, the more brittle it is. In small-particle form, it proves to be very reactive.
In air, hafnium forms a thin, passivating oxide layer that protects the metal from corrosion. Powdered hafnium, on the other hand, burns in air. Hafnium is extremely temperature resistant and is considered to be extremely robust against bases and acids.
WHAT IS THE CASE FOR BUYING HAFNIUM?
Facts about Hafnium!
When cutting steel with plasma torches today, a new technology is often used in which hafnium plays a supporting role. A small component made of pure hafnium is integrated into the copper electrode. On the one hand, because this technology metal is extremely corrosion-resistant and has a high melting point, and on the other because hafnium has the property of releasing electrons into the air.
Boiling point4.603 °C

Extraction of hafnium
With a content of 5.6 ppm in the continental earth's crust, hafnium occurs with approximately the same frequency as gold or mercury. In 2020, annual global production of the sought-after strategy metal was about 84 metric tons, compared with only about 34 metric tons for high-purity hafnium. However, global hafnium reserves are estimated at more than 1 million tons. Today, a large part comes from Australia and South Africa.
The extraction of hafnium is extremely complex. It occurs exclusively as a foreign admixture in zirconium minerals such as zircon and alledeite and is difficult to separate from them. In ore processing, hafnium is extracted by ion exchange processes and then purified by vacuum distillation.
Applications
1 The adding of hafnium allows for the production of high-strength and extremely wear-resistant super alloys for aircraft turbines.
2 Hafnium is ideally suited for the production of control rods in nuclear reactors because the metal can absorb neutrons.
3 Compared with silicon, hafnium promises fewer leakage currents, greater speed and lower production costs.
4 Because hafnium emits a very bright light when burned, it is used to make flash lamps with particularly high luminous efficacy.
Other applications at a glance: Super alloys, innovative semiconductor technology, recrystallization of tungsten filaments.
Expert tip
"Like any technology metal, the development of demand for hafnium is very closely linked to the economic situation in the manufacturing sectors. If the economy develops positively, the price of the raw material will also rise. As the aircraft industry alone expects demand for more than 36,000 new passenger and cargo jets by 2033, buyers have good opportunities to profit from the expected availability bottlenecks.“ Thomas Grob, Tradium